Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
A Bipolar Junction Transistor is a three terminals active semiconductor device formed by two back-to-back p-n junctions. The three terminals are labeled base, emitter and collector. Its main function is the current amplification between the collector or emitter currents and the base current.
There are 2 types of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), the NPN and the PNP.
Circuit Analysis
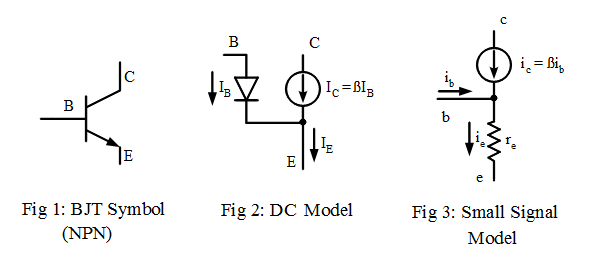
-
To analyse a transistor circuit,
- Do a DC analysis by redrawing the schematic
- replace the BJT symbol with its DC model.
- open circuit any capacitor and short circuit any inductor.
- If an AC analysis is required, redraw the schematic
- by replacing the BJT symbol with the small signal model.
- calculate re using IE from the DC analysis and vT=26 mV. \begin{equation} r_e = {v_{T} \over I_E} \end{equation} note that the AC analysis is only valid for vbe < vT
- short circuit any capacitor and open circuit any inductor. Short Circuit any DC power supply.
Single BJT Circuit Configuration
There are 3 configurations for the circuits with a single Bipolar Junction Transistor. They are the common emitter, common base and common collector circuits.
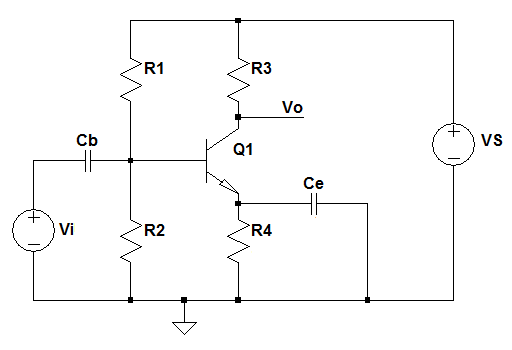
Analyse the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier
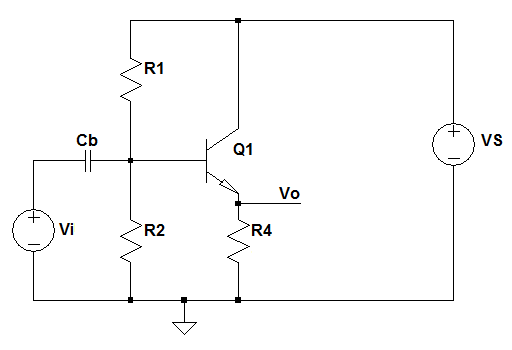
Analyse the BJT Common Collector Amplifier
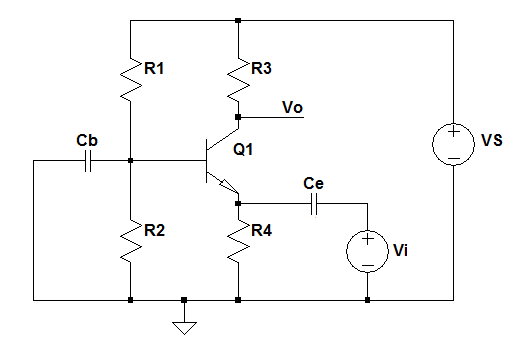
Analyse the BJT Common Base Amplifier
| Configuration Characteristics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common Emitter | Common Collector | Common Base | ||
| Input | Base | Base | Emitter | |
| Output | Collector | Emitter | Collector | |
| Input/Output Phase relationship | 180o | 0o | 0o | Voltage Gain | Medium | Unity | High |
| Current Gain | Medium | High | Unity | |
| Input Impedance | Medium | High | Low | |
| Output Impedance | Medium | Low | High | |